What determines how much coverage a climate study gets?
It probably goes without saying that it isn’t strongly related to the quality of the actual science, nor to the clarity of the writing. Appearing in one of the top journals does help (Nature, Science, PNAS and occasionally GRL), though that in itself is no guarantee. Instead, it most often depends on the ‘news’ value of the bottom line. Journalists and editors like stories that surprise, that give something ‘new’ to the subject and are therefore likely to be interesting enough to readers to make them read past the headline. It particularly helps if a new study runs counter to some generally perceived notion (whether that is rooted in fact or not). In such cases, the ‘news peg’ is clear.
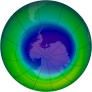
And so it was for the Steig et al “Antarctic warming” study that appeared last week. Mainstream media coverage was widespread and generally did a good job of covering the essentials. The most prevalent peg was the fact that the study appeared to reverse the “Antarctic cooling” meme that has been a staple of disinformation efforts for a while now.
[Read more…] about Warm reception to Antarctic warming story

 Browsing through the blogosphere recently, I came across an interesting little story about the scientific method, scientific progress, and un-scientific spin (h/t
Browsing through the blogosphere recently, I came across an interesting little story about the scientific method, scientific progress, and un-scientific spin (h/t 