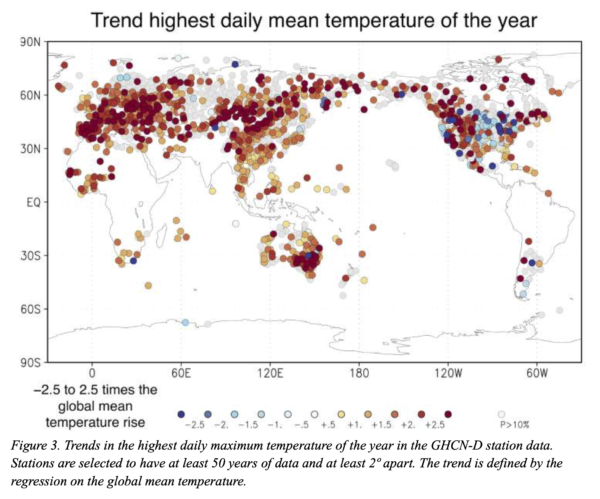
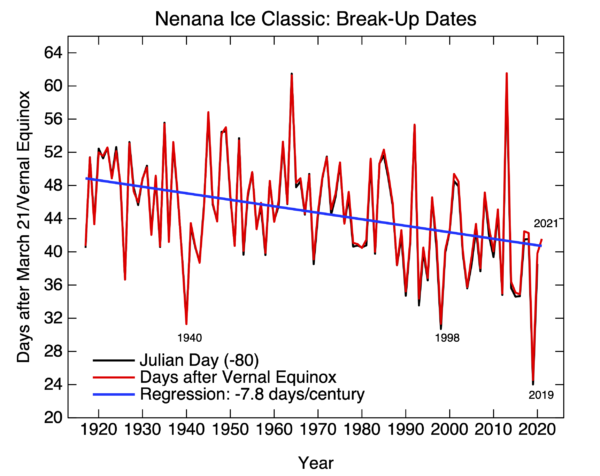
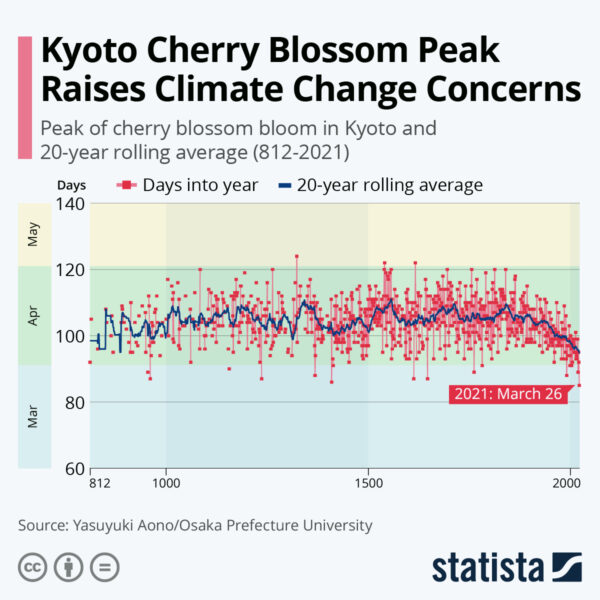
This month is IPCC month – the Sixth Assessment Report from Working Group 1 is out on Monday August 9. We’ll have some detailed comments once it’s out, but in the meantime, feel free to speculate widely (always considering that IPCC is restricted to assessing existing literature…).
Open thread – please stick to climate science topics.