There was a time at NASA when writing a letter to the paper without your director’s permission could get you fired. And no, I’m not talking about the last Bush administration.
[Read more…] about Steve Schneider’s first letter to the editor
Communicating Climate
Unforced variations: Apr 2011
This months open thread. There are some Items of potential interest::
- The fallout (and falling out) from the climate hearings yesterday (video) (liveblog)
- A good paper on science communication in Nature Climate Change
- A set of articles on the Medieval Climate Anomaly (MCA) in this month’s PAGES newsletter.
or whatever you like.
Making climate science more useful

The CORDEX initiative, as the abbreviation ‘COordinated Regional climate Downscaling Experiment‘ suggests, tries to bring together the community of regional climate modellers. At least, this initiative has got a blessing from the World Climate Research Programme WCRP.
I think the most important take-home message from the workshop is that the stake holders and end users of climate information should not look at just one simulation from global climate models, or just one downscaling method. This is very much in agreement with the recommendations from the IPCC Good Practice Guidance Paper. The main reason for this is the degree of uncertainties involved in regional climate modelling, as discussed in a previous post.
Friday round-up
Last week, Nature published another strong statement addressing the political/economic attack on climate science in an editorial titled “Into Ignorance“. It specifically criticized the right wing element of the U.S. Congress that is attempting to initiate legislation that would strip the US EPA of its powers to regulate greenhouse gases as pollutants. In so doing, it cited as an example the charade of a hearing conducted recently, including the Republicans’ disrespectful and ignorant attitude toward the science and scientists. Among many low points, this may have reached its nadir when a House member from Nebraska asked, smirkingly and out of the blue, whether nitrogen should be banned–presumably to make the point that atmospheric gases are all either harmless or outright beneficial, and hence, should not be regulated. Aside from the obvious difference that humans are not altering the nitrogen concentration of the atmosphere, as they are with (several) greenhouse gases, such a question boggles the mind in terms of the mindset that must exist to ask it in a public congressional hearing in the first place. But rarely are the ignorant and ideological bashful about showing it, regardless of who might be listening. In fact an increasing number seem to take it as a badge of honor.
There have been even more strongly worded editorials in the scientific literature recently as well. Trevors and Saier (2011)*, in a journal with a strong tradition of stating exactly where it stands with respect to public policy decisions and their effect on the environment, pull no punches in a recent editorial, describing the numerous societal problems caused when those with the limited perspective and biases born of a narrow economic outlook on the world, get control. These include the losses of critical thinking skills, social/community ethics, and the subsequent wise decision making and planning skills that lead a society to long-term health and stability.
Meanwhile, scientific bodies charged with understanding how the world actually works–instead of how they would imagine and proclaim it to–continue to issue official statements endorsing the consensus view that humans are strongly warming the planet in recent decades, primarily by greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere. Three years ago, we wondered whether geologists in general have a different view on climate change to the climate research community. A recent statement from the U.K. Geological Society, however, suggests that our impressions perhaps were not well-founded.
Notwithstanding these choices of ignorance, many other organizations continue apace with many worthwhile and diverse goals of how to deal with the problem. Here are a few links that we have run across in the last week or two that may be of interest to those interested in sustainability and adaptation. Please note the imminent deadlines on some of these.
The CDKN International Research Call on Climate Compatible Development:
The Climate Frontlines call for abstracts for a July conference in Mexico City on the theme “Indigenous Peoples, Marginalized Populations and Climate Change” [Apologies: the official deadline for abstracts has apparently passed; view this is a conference announcement]
George Mason University’s call for votes on the Climate Change Communicator of the Year
*Trevors, J.T & Saier Jr., M.H. 2011. A vaccine against ignorance? Water, Air and Soil Pollution, DOI 10.1007/s11270-011-0773-1.
Blogging climate scientists
The newest arrival in the climate science blogosphere is Isaac Held. This is notable in a number of respects. First, Isaac is a top-tier climate scientist who is hugely respected in the community. For him to decide that it is worth his time to blog on the science should be an important signal for other scientists. Secondly, Isaac is a federal NOAA employee at GFDL in Princeton, and the blog is on the official GFDL website.
Live-blogging the climate science hearings
I will be live-blogging the House Energy and Commerce committee hearings on climate science with Eli Kintisch. The details are available here, and there should be a live feed from the committee website from 10am.
Eli and I did this last year for the last Democrat-run hearings, and it went quite well – a little like a play-by-play from Eli and some background analysis/cites from me. People can ask questions and comment in real time and depending on how busy it gets, they might get a response.
As usual, this hearing will likely be long on political grandstanding and short on informed discussion, but there might be some gems. Of the witnesses, John Christy and Roger Pielke Sr. are the main witnesses for the majority side, while Richard Somerville, Francis Zwiers and Chris Field are the Dem invitees. There is newcomer to the roster (at least to me), in Knute Nadelhoffer, who presumably will discuss climate change impacts on biological systems (but I don’t really know). There is one out-of-left-field witness, Donald Roberts, who is a serially wrong DDT advocate who is probably there in order to dismiss environmental regulation in general, following the well-worn strategy described in Oreskes and Conway’s “Merchants of Doubt” (Chapter 7 on the revisionist attacks on Rachel Carson) (NB. DDT-related arguments are off topic for this blog, but for background of the specifics of the DDT ‘meme’ see this summary, and interested commenters are encouraged to go to Deltoid).
Anyway, for those who are aficionados of science as contact sport (TM, Steve Schneider), it might be fun.
Update: This was also live-blogged at ClimateCentral and twittered by UCS.
Going to extremes
There are two new papers in Nature this week that go right to the heart of the conversation about extreme events and their potential relationship to climate change. This is a complex issue, and one not well-suited to soundbite quotes and headlines, and so we’ll try and give a flavour of what the issues are and what new directions these new papers are pointing towards.
[Read more…] about Going to extremes
The Starship vs. Spaceship Earth
Eric Steig & Ray Pierrehumbert

It turns out that Brower has wondered the same thing, and in a recent article in The Atlantic, he speculates on the answer. “How could someone as smart as Freeman Dyson,” writes Brower, “be so wrong about climate change and other environmental concerns..?”
[Read more…] about The Starship vs. Spaceship Earth
West Antarctica: still warming
The temperature reconstruction of O’Donnell et al. (2010) confirms that West Antarctica is warming — but underestimates the rate
Eric Steig
At the end of my post last month on the history of Antarctic science I noted that I had an initial, generally favorable opinion of the paper by O’Donnell et al. in the Journal of Climate. O’Donnell et al. is the peer-reviewed outcome of a series of blog posts started two years ago, mostly aimed at criticizing the 2009 paper in Nature, of which I was the lead author. As one would expect of a peer-reviewed paper, those obviously unsupportable claims found in the original blog posts are absent, and in my view O’Donnell et al. is a perfectly acceptable addition to the literature. O’Donnell et al. suggest several improvements to the methodology we used, most of which I agree with in principle. Unfortunately, their actual implementation by O’Donnell et al. leaves something to be desired, and yield a result that is in disagreement with independent evidence for the magnitude of warming, at least in West Antarctica.
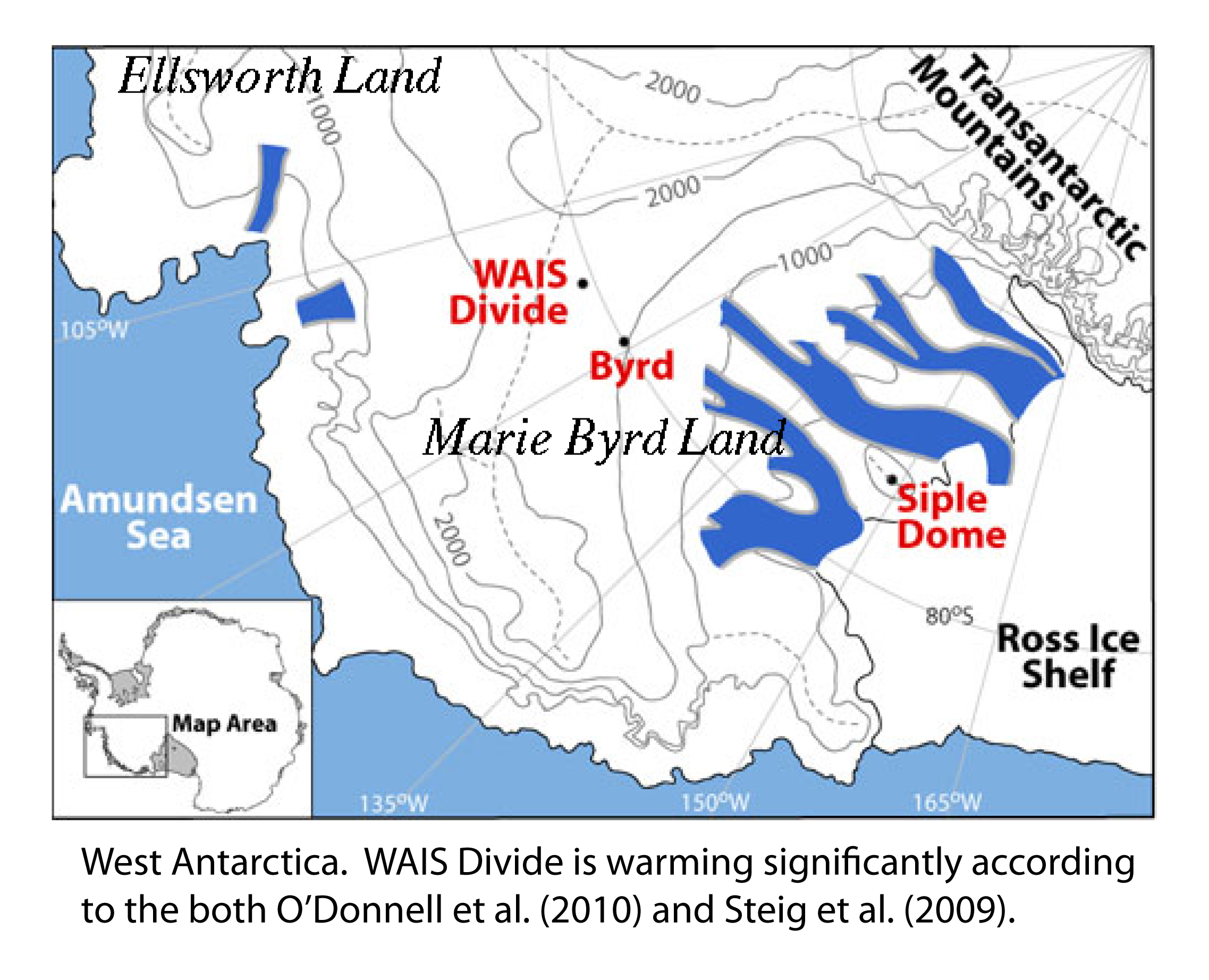
[Read more…] about West Antarctica: still warming
The obvious answer
Climate science appears to be just like any other science. At least, this is the conclusion from a fresh publication by Marianne Ryghaug and Tomas Moe Skjølsvold (“The global warming of climate science: Climategate and the construction of scientific facts” in International studies in the philosophy of science). This finding is not news to the research community, but this analysis still hints that everything is not as it should be – because why would anyone report from a crime scene if the alleged crime has not even been committed?