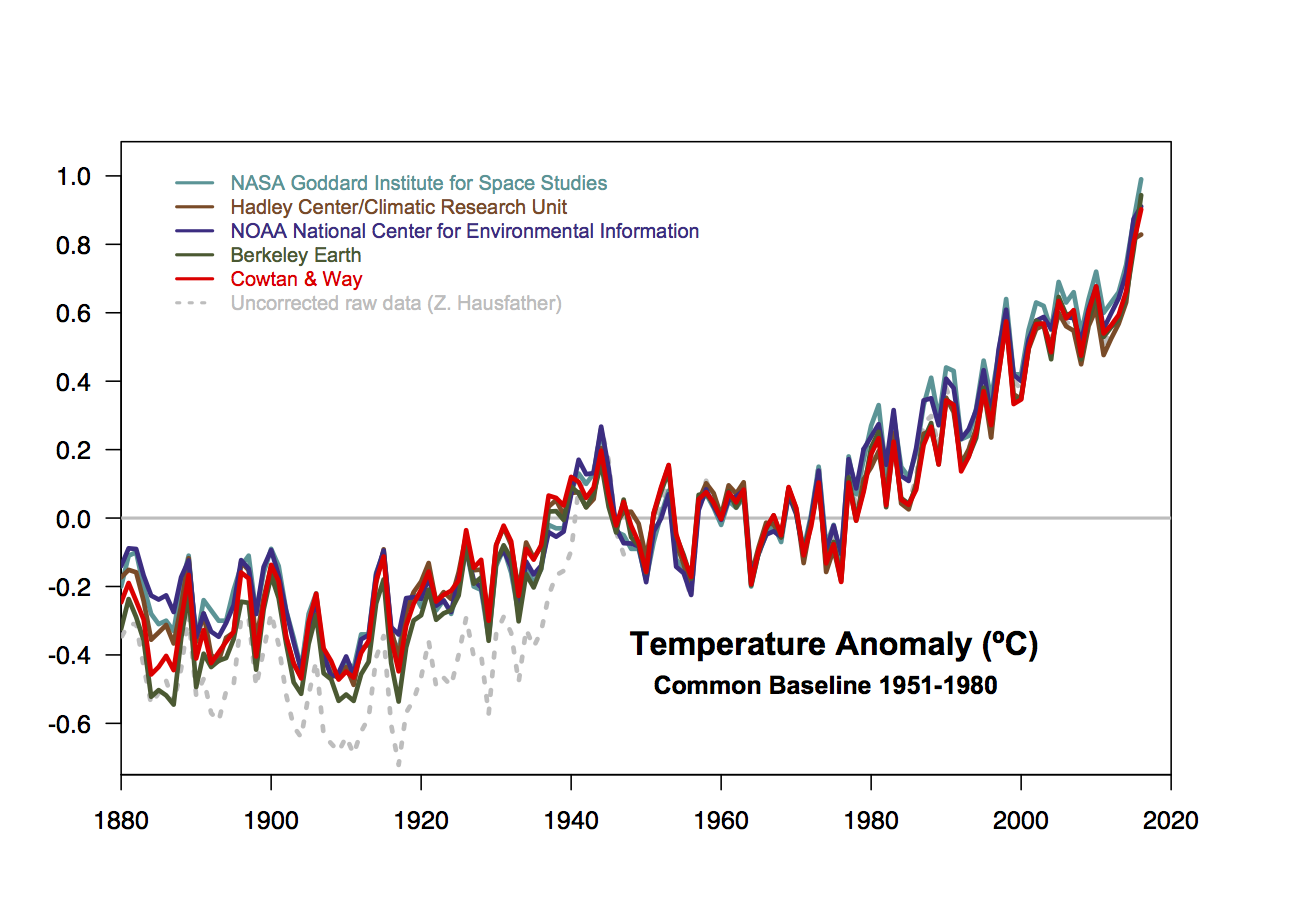
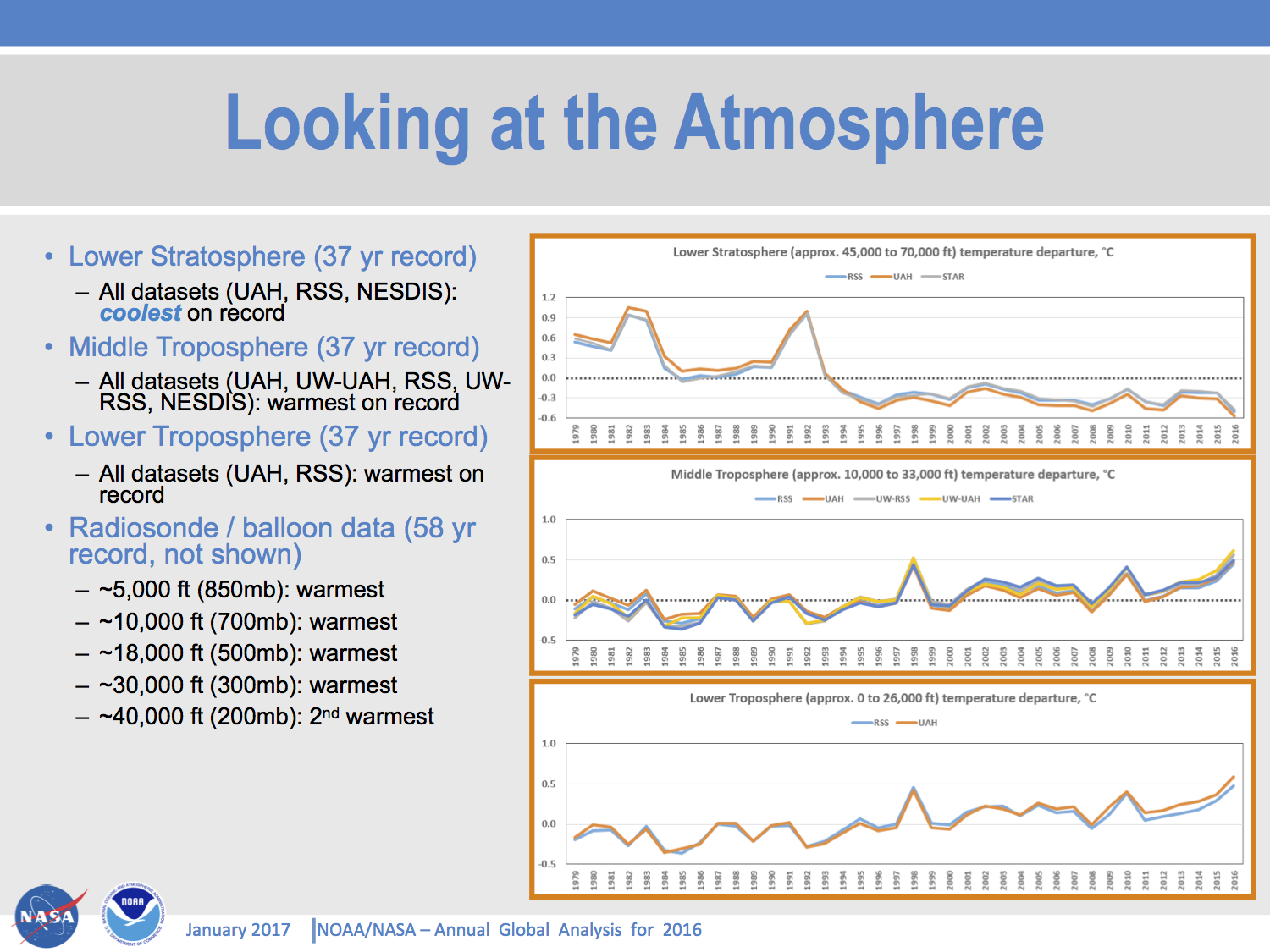
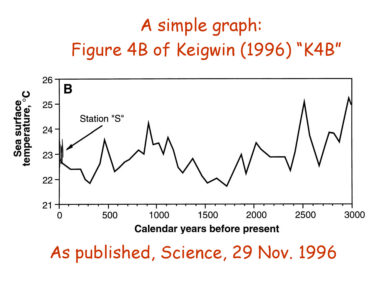
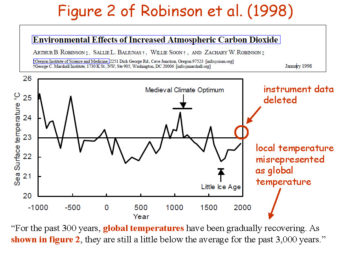
Do we need a new venue for post-publication comments and replications?
Social media is full of commentary (of varying degrees of seriousness) on the supposed replication crisis in science. Whether this is really a crisis, or just what is to be expected at the cutting edge is unclear (and may well depend on the topic and field). But one thing that is clear from all the discussion is that it’s much too hard to publish replications, or even non-replications, in the literature. Often these efforts have to be part of a new paper that has to make its own independent claim to novelty before it can get in the door and that means that most attempted replications don’t get published at all.
This is however just a subset of the difficulty that exists in getting any kind of comment on published articles accepted. Having been involved in many attempts – in the original journal or as a new paper – some successful, many not, it has become obvious to me that the effort to do so is wholly disproportionate to the benefits for the authors, and is thus very effectively discouraged.
The overall mismatch between the large costs/minimal benefit for the commenters, compared to the real benefits for the field, suggests that something really needs to change.
I have thought for a long time that an independent journal venue for comments would be a good idea, but a tweet by Katharine Hayhoe last weekend made me realize that the replication issue might be well served by a similar approach. So, here’s a proposal for a new journal.
Commentary And Replication in Earth Science (C.A.R.E.S.)
[Read more…] about Someone C.A.R.E.S.
References
- G. Foster, J.D. Annan, G.A. Schmidt, and M.E. Mann, "Comment on “Heat capacity, time constant, and sensitivity of Earth's climate system” by S. E. Schwartz", Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, vol. 113, 2008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009373
- G.A. Schmidt, "Spurious correlations between recent warming and indices of local economic activity", International Journal of Climatology, vol. 29, pp. 2041-2048, 2009. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/joc.1831