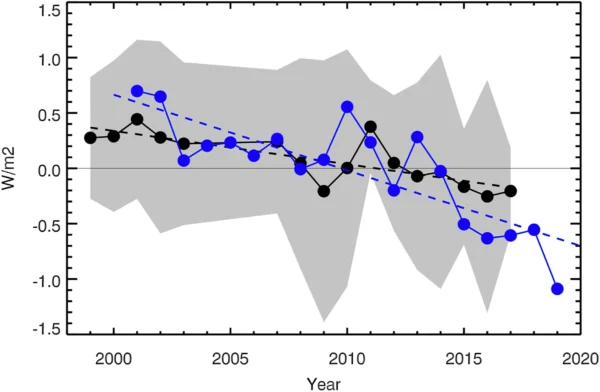
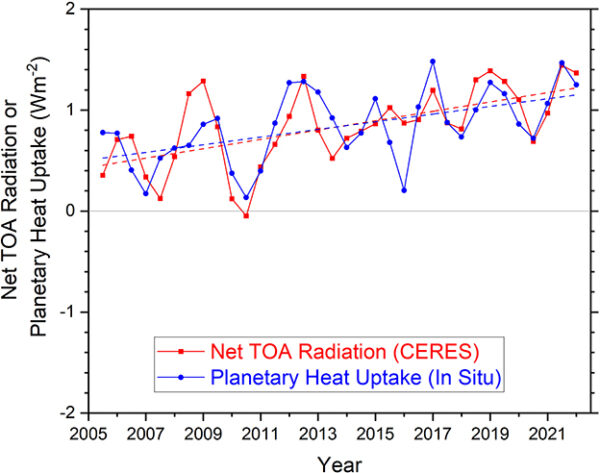
A new paper from Scafetta and it’s almost as bad as the last one.
Back in March, we outlined how a model-observations comparison paper in GRL by Nicola Scafetta (Scafetta, 2022a) got wrong basically everything that one could get wrong (the uncertainty in the observations, the internal variability in the models, the statistical basis for comparisons – the lot!). Now he’s back with a new paper in a different journal (Scafetta, 2022b) that could be seen as trying to patch the holes in the first one, but while he makes some progress, he now adds some new errors while attempting CPR on his original conclusions.
[Read more…] about Scafetta comes back for moreReferences
- N. Scafetta, "Advanced Testing of Low, Medium, and High ECS CMIP6 GCM Simulations Versus ERA5‐T2m", Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 49, 2022. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2022GL097716
- N. Scafetta, "CMIP6 GCM ensemble members versus global surface temperatures", Climate Dynamics, vol. 60, pp. 3091-3120, 2022. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06493-w