A few weeks ago, we’ve argued in a paper in Nature that the Atlantic overturning circulation (sometimes popularly dubbed the Gulf Stream System) has weakened significantly since the late 19th Century, with most of the decline happening since the mid-20th Century. We have since received much praise for our study from colleagues around the world (thanks for that). But there were also some questions and criticisms in the media, so I’d like to present a forum here for discussing these questions and hope that others (particularly those with a different view) will weigh in in the comments section below. [Read more…] about If you doubt that the AMOC has weakened, read this
IPCC
The Alsup Aftermath
The presentations from the Climate Science tutorial last month have all been posted (links below), and Myles Allen (the first presenter for the plaintiffs) gives his impression of the events.
[Read more…] about The Alsup Aftermath
IPCC Communication handbook
A new handbook on science communication came out from IPCC this week. Nominally it’s for climate science related communications, but it has a wider application as well. This arose mainly out of an “Expert meeting on Communication” that IPCC held in 2016.
6 principles to help IPCC scientists better communicate their work
There was a Guardian article on it as well.
The six principles are pretty straightforward:
- Be a confident communicator
- Talk about the real world, not abstract ideas
- Connect with what matters to your audience
- Tell a human story
- Lead with what you know
- Use the most effective visual communication
Each is supported with references to the relevant literature and with climate-related (“real world”) examples that are themselves confidently communicated with effective visuals.
But what do people think? Is this a useful addition to the literature on communication? Anything you think doesn’t work? or that perhaps surprises you?
PS. I’m perhaps a little biased because they use a Peter Essick photo for their cover art that was also in my book.
1.5ºC: Geophysically impossible or not?
Guest commentary by Ben Sanderson
Millar et al’s recent paper in Nature Geoscience has provoked a lot of lively discussion, with the authors of the original paper releasing a statement to clarify that their paper did not suggest that “action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is no longer urgent“, rather that 1.5ºC (above the pre-industrial) is not “geophysically impossible”.
The range of post-2014 allowable emissions for a 66% chance of not passing 1.5ºC in Millar et al of 200-240GtC implies that the planet would exceed the threshold after 2030 at current emissions levels, compared with the AR5 analysis which would imply most likely exceedance before 2020. Assuming the Millar numbers are correct changes 1.5ºC from fantasy to merely very difficult.
But is this statement overconfident? Last week’s post on Realclimate raised a couple of issues which imply that both the choice of observational dataset and the chosen pre-industrial baseline period can influence the conclusion of how much warming the Earth has experienced to date. Here, I consider three aspects of the analysis – and assess how they influence the conclusions of the study.
[Read more…] about 1.5ºC: Geophysically impossible or not?
Why extremes are expected to change with a global warming
Joanna Walters links extreme weather events with climate change in a recent article in the Guardian, however, some reservations have been expressed about such links in past discussions.
For example, we discussed the connection between single storms and global warming in the post Hurricanes and Global Warming – Is there a connection?, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has issued a statement, and Mike has recently explained the connection in the Guardian.
[Read more…] about Why extremes are expected to change with a global warming
Something Harde to believe…
A commenter brings news of an obviously wrong paper that has just appeared in Global and Planetary Change. The paper purports to be a radical revision of our understanding of the carbon cycle by Hermann Harde. The key conclusions are (and reality in green):
- The average residence time of CO2 in the atmosphere is found to be 4 years.
[The residence time for an individual molecule is not the same as the perturbation response time of the carbon cycle which has timescales of decades to thousands of years.]
- The anthropogenic fraction of CO2 in the atmosphere is only 4.3%.
[Actually, it’s 30%.]
- Human emissions only contribute 15% to the CO2 increase over the Industrial Era.
[It’s all of it.]
Since these points contradict multiple independent sources of evidence, I can, without hesitation, predict that there are fundament flaws in this paper that will raise serious questions about the quality of the peer-review that this paper went through. Oddly, this paper is labeled as an “Invited Research Article” and so maybe some questions might be asked of the editor responsible too.
Notwithstanding our last post on the difficulty in getting comments published, this paper is crying out for one.
But this kind of thing has been done before, does not require any great sophistication or computer modeling to rebut, and has come up so many times before (Salby (also here), Beck, Segalstad, Jaworowski etc.), that perhaps a crowd-sourced rebuttal would be useful.
So, we’ll set up an overleaf.com page for this (a site for collaborative LaTeX projects), and anyone who wants to contribute should put the gist of their point in the comments and we’ll send the link so you can add it to the draft. Maybe the citizen scientists among you can pull together a rebuttal faster than the professionals?
Update: The crowd-sourced comment has appeared Köhler et al (2018).
References
- H. Harde, "Scrutinizing the carbon cycle and CO2 residence time in the atmosphere", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 152, pp. 19-26, 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.02.009
- P. Köhler, J. Hauck, C. Völker, D.A. Wolf-Gladrow, M. Butzin, J.B. Halpern, K. Rice, and R.E. Zeebe, "Comment on “ Scrutinizing the carbon cycle and CO 2 residence time in the atmosphere ” by H. Harde", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 164, pp. 67-71, 2018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.09.015
Comparing models to the satellite datasets
How should one make graphics that appropriately compare models and observations? There are basically two key points (explored in more depth here) – comparisons should be ‘like with like’, and different sources of uncertainty should be clear, whether uncertainties are related to ‘weather’ and/or structural uncertainty in either the observations or the models. There are unfortunately many graphics going around that fail to do this properly, and some prominent ones are associated with satellite temperatures made by John Christy. This post explains exactly why these graphs are misleading and how more honest presentations of the comparison allow for more informed discussions of why and how these records are changing and differ from models.
[Read more…] about Comparing models to the satellite datasets
Blizzard Jonas and the slowdown of the Gulf Stream System
Blizzard Jonas on the US east coast has just shattered snowfall records. Both weather forecasters and climate experts have linked the high snowfall amounts to the exceptionally warm sea surface temperatures off the east coast. In this post I will examine a related question: why are sea surface temperatures so high there, as shown in the snapshot from Climate Reanalyzer below?
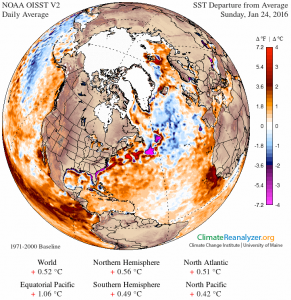
I will argue that this warmth (as well as the cold blob in the subpolar Atlantic) is partly due to a slowdown of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), sometimes referred to as the Gulf Stream System, in response to global warming. There are two points to this argument:
[Read more…] about Blizzard Jonas and the slowdown of the Gulf Stream System
Marvel et al (2015) Part 1: Reconciling estimates of climate sensitivity
This post is related to the substantive results of the new Marvel et al (2015) study. There is a separate post on the media/blog response.
The recent paper by Kate Marvel and others (including me) in Nature Climate Change looks at the different forcings and their climate responses over the historical period in more detail than any previous modeling study. The point of the paper was to apply those results to improve calculations of climate sensitivity from the historical record and see if they can be reconciled with other estimates. But there are some broader issues as well – how scientific anomalies are dealt with and how simulation can be used to improve inferences about the real world. It also shines a spotlight on a particular feature of the IPCC process…
[Read more…] about Marvel et al (2015) Part 1: Reconciling estimates of climate sensitivity
References
- K. Marvel, G.A. Schmidt, R.L. Miller, and L.S. Nazarenko, "Implications for climate sensitivity from the response to individual forcings", Nature Climate Change, vol. 6, pp. 386-389, 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2888
And the winner is…
Remember the forecast of a temporary global cooling which made headlines around the world in 2008? We didn’t think it was reliable and offered a bet. The forecast period is now over: we were right, the forecast was not skillful.
Back around 2007/8, two high-profile papers claimed to produce, for the first time, skilful predictions of decadal climate change, based on new techniques of ocean state initialization in climate models. Both papers made forecasts of the future evolution of global mean and regional temperatures. The first paper, Smith et al. (2007), predicted “that internal variability will partially offset the anthropogenic global warming signal for the next few years. However, climate will continue to warm, with at least half of the years after 2009 predicted to exceed the warmest year currently on record.” The second, Keenlyside et al., (2008), forecast in contrast that “global surface temperature may not increase over the next decade, as natural climate variations in the North Atlantic and tropical Pacific temporarily offset the projected anthropogenic warming.”
This month marks the end of the forecast period for Keenlyside et al and so their forecasts can now be cleanly compared to what actually happened. This is particularly interesting to RealClimate, since we offered a bet to the authors on whether the results would be accurate based on our assessment of their methodology. They ignored our offer but now the time period of the bet has passed, it’s worth checking how it would have gone.
[Read more…] about And the winner is…
References
- D.M. Smith, S. Cusack, A.W. Colman, C.K. Folland, G.R. Harris, and J.M. Murphy, "Improved Surface Temperature Prediction for the Coming Decade from a Global Climate Model", Science, vol. 317, pp. 796-799, 2007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1139540
- N.S. Keenlyside, M. Latif, J. Jungclaus, L. Kornblueh, and E. Roeckner, "Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic sector", Nature, vol. 453, pp. 84-88, 2008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature06921