Joanna Walters links extreme weather events with climate change in a recent article in the Guardian, however, some reservations have been expressed about such links in past discussions.
For example, we discussed the connection between single storms and global warming in the post Hurricanes and Global Warming – Is there a connection?, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has issued a statement, and Mike has recently explained the connection in the Guardian.
[Read more…] about Why extremes are expected to change with a global warming
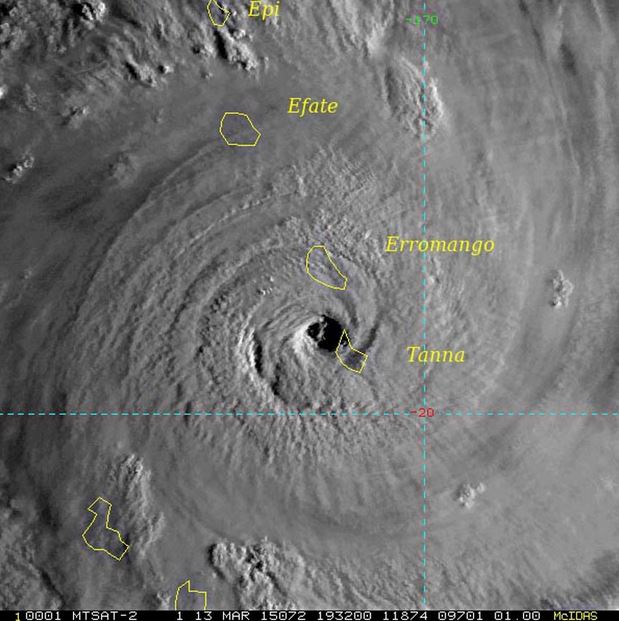

 The Dvorak Technique has been used for many years at all global tropical cyclone forecast centers and has been shown in many cases to yield a good estimate of maximum TC wind speed, when applied properly
The Dvorak Technique has been used for many years at all global tropical cyclone forecast centers and has been shown in many cases to yield a good estimate of maximum TC wind speed, when applied properly 

 If you are a RealClimate regular, you are undoubtedly aware of our ongoing interest in
If you are a RealClimate regular, you are undoubtedly aware of our ongoing interest in