Guest commentary by Karsten Haustein, U. Oxford, and Peter Jacobs (George Mason University).
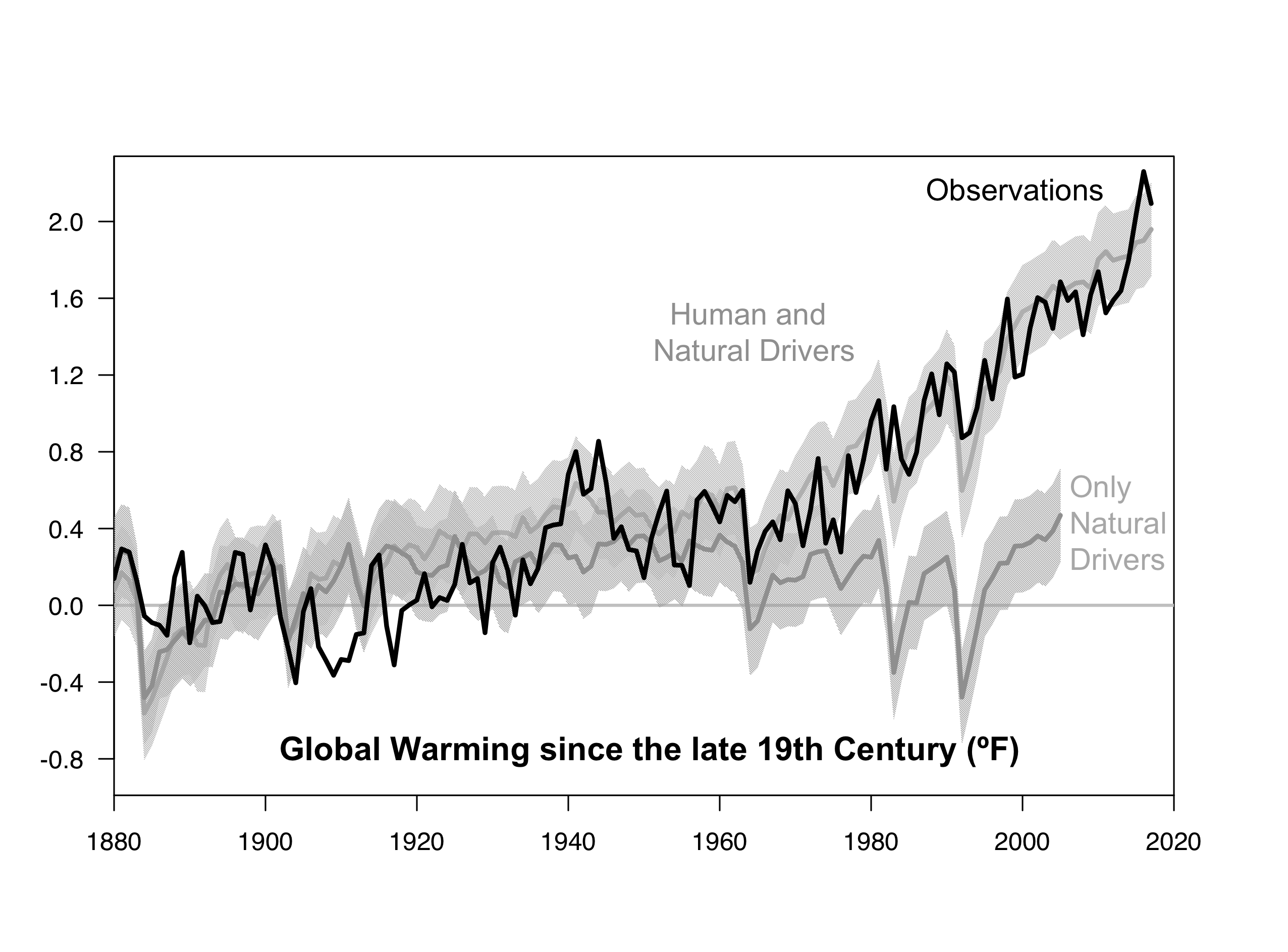
One of the perennial issues in climate research is how big a role internal climate variability plays on decadal to longer timescales. A large role would increase the uncertainty on the attribution of recent trends to human causes, while a small role would tighten that attribution. There have been a number of attempts to quantify this over the years, and we have just published a new study (Haustein et al, 2019) in the Journal of Climate addressing this question.
Using a simplified climate model, we find that we can reproduce temperature observations since 1850 and proxy-data since 1500 with high accuracy. Our results suggest that multidecadal ocean oscillations are only a minor contributing factor in the global mean surface temperature evolution (GMST) over that time. The basic results were covered in excellent articles in CarbonBrief and Science Magazine, but this post will try and go a little deeper into what we found.
[Read more…] about Unforced Variations vs Forced Responses?References
- K. Haustein, F.E.L. Otto, V. Venema, P. Jacobs, K. Cowtan, Z. Hausfather, R.G. Way, B. White, A. Subramanian, and A.P. Schurer, "A Limited Role for Unforced Internal Variability in Twentieth-Century Warming", Journal of Climate, vol. 32, pp. 4893-4917, 2019. http://dx.doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0555.1