Summer 2018 saw an unprecedented spate of extreme weather events, from the floods in Japan, to the record heat waves across North America, Europe and Asia, to wildfires that threatened Greece and even parts of the Arctic. The heat and drought in the western U.S. culminated in the worst California wildfire on record. This is the face of climate change, I commented at the time.
Some of the connections with climate change here are pretty straightforward. One of the simplest relationships in all of atmospheric science tells us that the atmosphere holds exponentially more moisture as temperatures increase. Increased moisture means potentially for greater amounts of rainfall in short periods of time, i.e. worse floods. The same thermodynamic relationship, ironically, also explains why soils evaporate exponentially more moisture as ground temperatures increase, favoring more extreme drought in many regions. Summer heat waves increase in frequency and intensity with even modest (e.g. the observed roughly 2F) overall warming owing to the behavior of the positive “tail” of the bell curve when you shift the center of the curve even a small amount. Combine extreme heat and drought and you get more massive, faster-spreading wildfires. It’s not rocket science.
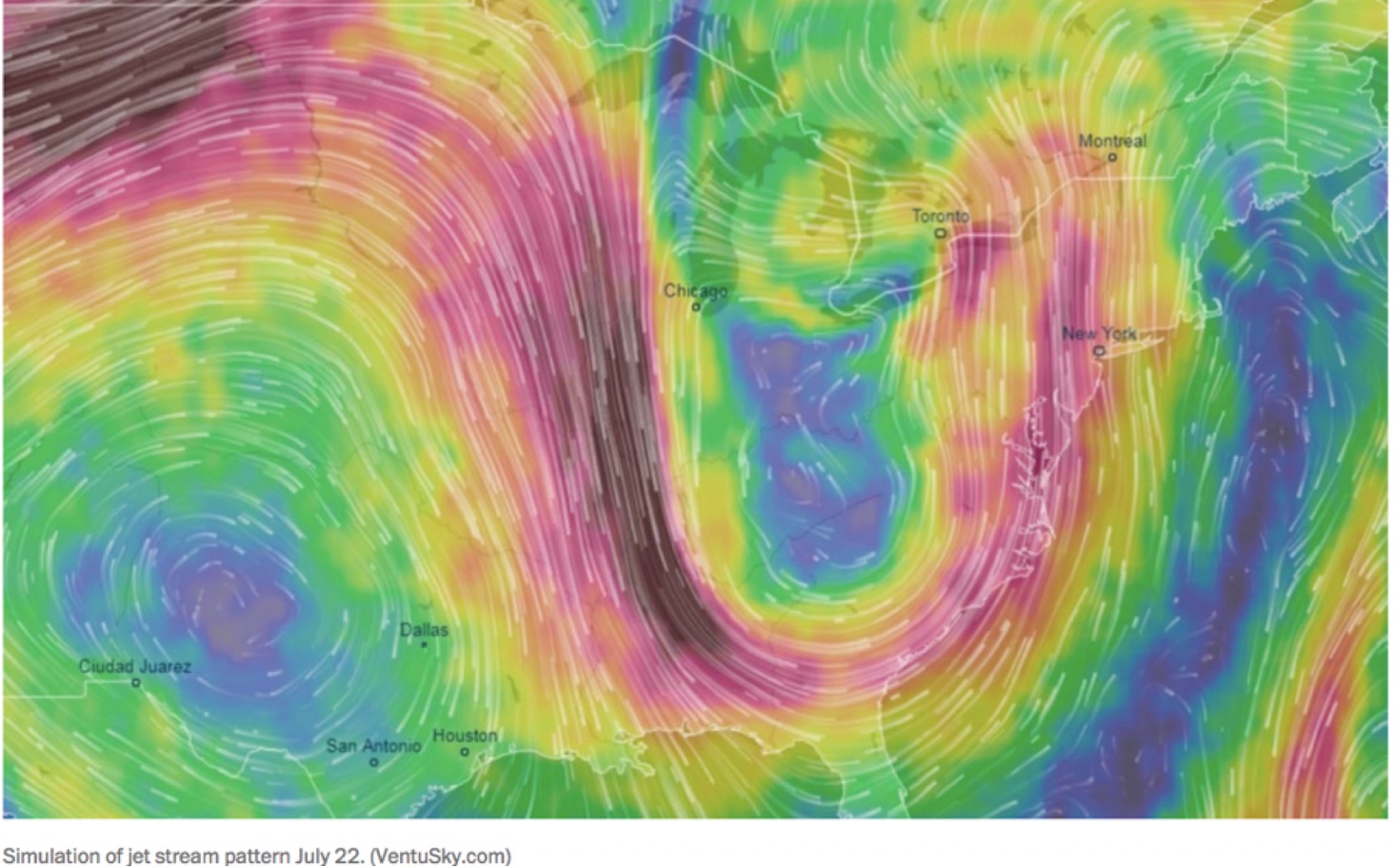
But there is more to the story. Because what made these events so devastating was not just the extreme nature of the meteorological episodes but their persistence. When a low-pressure center stalls and lingers over the same location for days at a time, you get record accumulation of rainfall and unprecedented flooding. That’s what happened with Hurricane Harvey last year and Hurricane Florence this year. It is also what happened with the floods in Japan earlier this summer and the record summer rainfall we experienced this summer here in Pennsylvania. Conversely, when a high-pressure center stalls over the same location, as happened in California, Europe, Asia and even up into the European Arctic this past summer, you get record heat, drought and wildfires.
Scientists such as Jennifer Francis have linked climate change to an increase in extreme weather events, especially during the winter season when the jet stream and “polar vortex” are relatively strong and energetic. The northern hemisphere jet stream owes its existence to the steep contrast in temperature in the middle latitudes (centered around 45N) between the warm equator and the cold Arctic. Since the Arctic is warming faster than the rest of the planet due to the melting of ice and other factors that amplify polar warming, that contrast is decreasing and the jet stream is getting slower. Just like a river traveling over gently sloping territory tends to exhibit wide meanders as it snakes its way toward the ocean, so too do the eastward-migrating wiggles in the jet stream (known as Rossby waves) tend to get larger in amplitude when the temperature contrast decreases. The larger the wiggles in the jet stream the more extreme the weather, with the peaks corresponding to high pressure at the surface and the troughs low pressure at the surface. The slower the jet stream, the longer these extremes in weather linger in the same locations, giving us more persistent weather extremes.
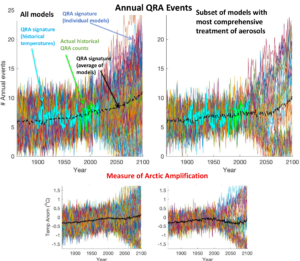
Something else happens in addition during summer, when the poleward temperature contrast is especially weak. The atmosphere can behave like a “wave guide”, trapping the shorter wavelength Rossby waves (those that that can fit 6 to 8 full wavelengths in a complete circuit around the Northern Hemisphere) to a relatively narrow range of latitudes centered in the mid-latitudes, preventing them from radiating energy away toward lower and higher latitudes. That allows the generally weak disturbances in this wavelength range to intensify through the physical process of resonance, yielding very large peaks and troughs at the sub-continental scale, i.e. unusually extreme regional weather anomalies. The phenomenon is known as Quasi-Resonant Amplification or “QRA”, and (see Figure below).
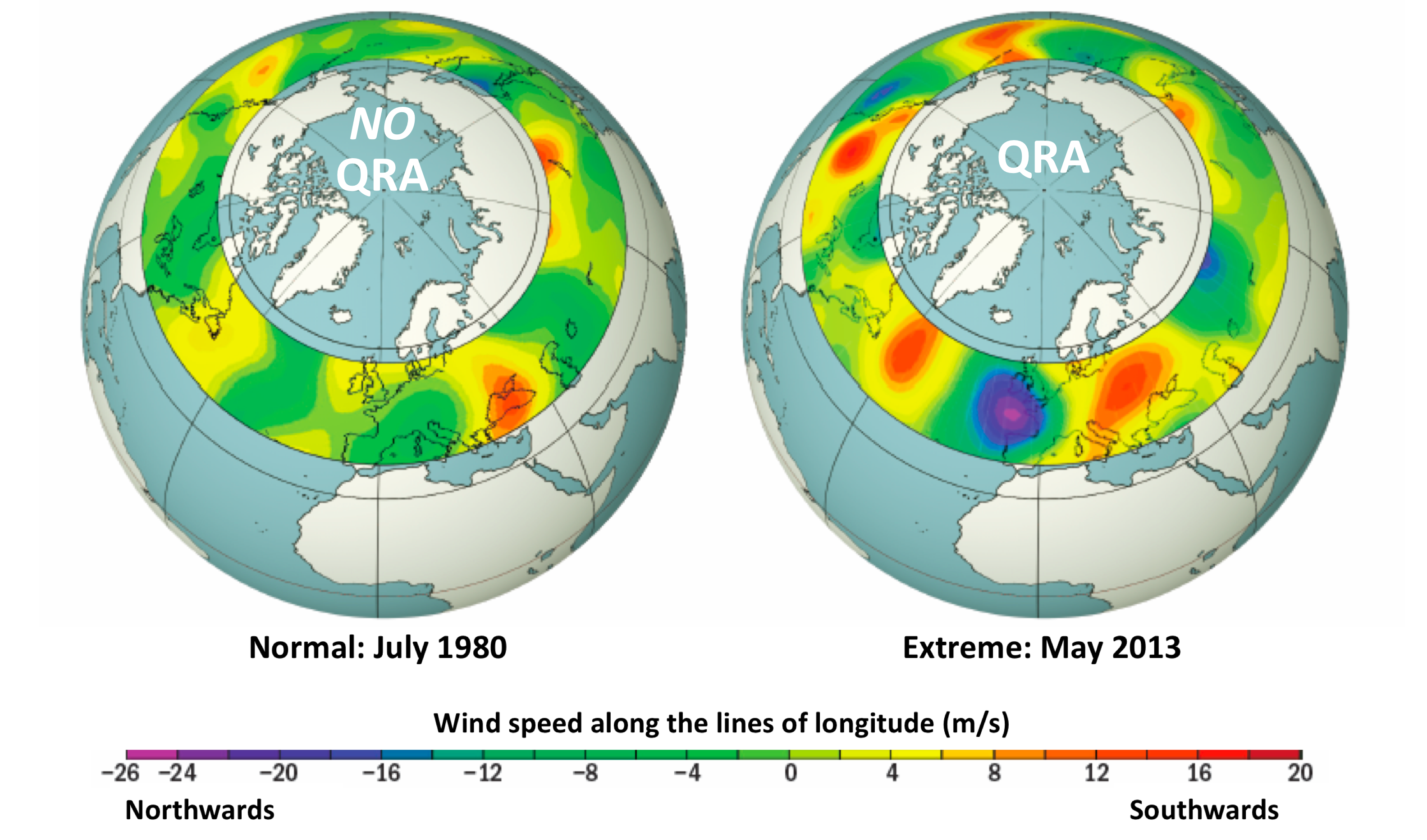
Many of the most damaging extreme summer weather events in recent decades have been associated with QRA, including the 2003 European heatwave, the 2010 Russian heatwave and wildfires and Pakistan floods (see below), and the 2011 Texas/Oklahoma droughts. More recent examples include the 2013 European floods, the 2015 California wildfires, the 2016 Alberta wildfires and, indeed, the unprecedented array of extreme summer weather events we witnessed this past summer.
The increase in the frequency of these events over time is seen to coincide with an index of Arctic amplification (the difference between warming in the Arctic and the rest of the Northern Hemisphere), suggestive of a connection (see Figure below).
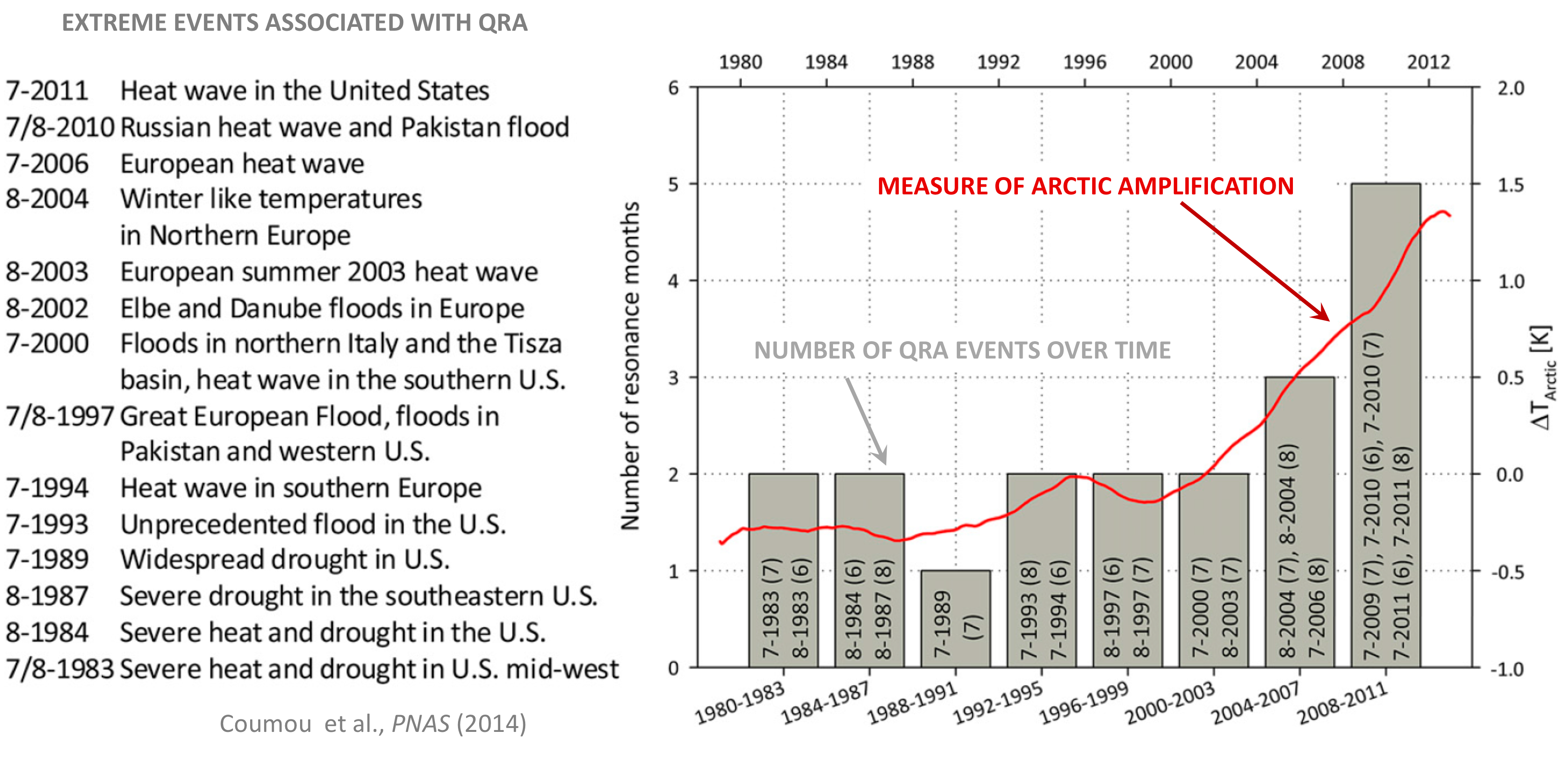
Last year we (me and a team of collaborators including RealClimate colleague Stefan Rahmstorf) published an article in the Nature journal Scientific Reports demonstrating that the same pattern of amplified Arctic warming (“Arctic Amplification”) that is slowing down the jet stream is indeed also increasing the frequency of QRA episodes. That means regional weather extremes that persist longer during summer when the jet stream is already at its weakest. Based on an analysis of climate observations and historical climate simulations, we concluded that the “signal” of human influence on QRA has likely emerged from the “noise” of natural variability over the past decade and a half. In summer 2018, I would argue, that signal was no longer subtle. It played out in real time on our television screens and newspaper headlines in the form of an unprecedented hemisphere-wide pattern of extreme floods, droughts, heat waves and wildfires.
In a follow-up article just published in the AAAS journal Science Advances, we look at future projections of QRA using state-of-the-art climate model simulations. It is important to note that that one cannot directly analyze QRA behavior in a climate model simulation for technical reasons. Most climate models are run at grid resolutions of a degree in latitude or more. The physics that characterizes QRA behavior of Rossby Waves faces a stiff challenge when it comes to climate models because it involves the second mathematical derivative of the jet stream wind with respect to latitude. Errors increase dramatically when you calculate a numerical first derivative from gridded fields and even more so when you calculate a second derivative. Our calculations show that the critical term mentioned above suffers from an average climate model error of more than 300% relative to observations. By contrast, the average error of the models is less than a percent when it comes to latitudinal temperature averages and still only about 30% when it comes to the latitudinal derivative of temperature.
That last quantity is especially relevant because QRA events have been shown to have a well-defined signature in terms of the latitudinal variation in temperature in the lower atmosphere. Through a well-established meteorological relationship known as the thermal wind, the magnitude of the jet stream winds is in fact largely determined by the average of that quantity over the lower atmosphere. And as we have seen above, this quantity is well captured by the models (in large part because the change in temperature with latitude and how it responds to increasing greenhouse gas concentrations depends on physics that are well understood and well represented by the climate models).
These findings, incidentally have broader implications. First of all, climate model-based studies used to assess the degree to which current extreme weather events can be attributed to climate change are likely underestimating the climate change influence. One model-based study for example suggested that climate change only doubled the likelihood of the extreme European heat wave this summer. As I commented at the time, that estimate is likely too low for it doesn’t account for the role that we happen to know, in this case, that QRA played in that event. Similarly, climate models used to project future changes in extreme weather behavior likely underestimate the impact that future climate changes could have on the incidence of persistent summer weather extremes like those we witnessed this past summer.
So what does our study have to say about the future? We find that the incidence of QRA events would likely continue to increase at the same rate it has in recent decades if we continue to simply add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. But there’s a catch: The future emissions scenarios used in making future climate projections must also account for factors other than greenhouse gases. Historically, for example, the use of old coal technology that predates the clean air acts produced sulphur dioxide gas which escapes into the atmosphere where it reacts with other atmospheric constituents to form what are known as aerosols.
These aerosols caused acid rain and other environmental problems in the U.S. before factories in the 1970s were required to install “scrubbers” to remove the sulphur dioxide before it leaves factory smokestacks. These aerosols also reflect incoming sunlight and so have a cooling effect on the surface in the industrial middle-latitudes where they are produced. Some countries, like China, are still engaged in the older, dirtier-form of coal burning. If we continue with business-as-usual burning of fossil fuels, but countries like China transition to more modern “cleaner” coal burning to avoid air pollution problems, we are likely to see a substantial drop in aerosols over the next half century. Such an assumption is made in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)’s “RCP 8.5” scenario—basically, a “business as usual” future emissions scenario which results in more than a tripling of carbon dioxide concentrations relative to pre-industrial levels (280 parts per million) and roughly 4-5C (7-9F) of planetary warming by the end of the century.
As a result, the projected disappearance of cooling aerosols in the decades ahead produces an especially large amount of warming in middle-latitudes in summer (when there is the most incoming sunlight to begin with, and, thus, the most sunlight to reflect back to space). Averaged across the various IPCC climate models there is even more warming in mid-latitudes than in the Arctic—in other words, the opposite of Arctic Amplification i.e. Arctic De-amplification (see Figure below). Later in the century after the aerosols disappear greenhouse warming once again dominates and we again see an increase in QRA events.
So, is there any hope to avoid future summers like the summer of 2018? Probably not. But in the scenario where we rapidly move away from fossil fuels and stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations below 450 parts per million, giving us a roughly 50% chance of averting 2C/3.6F planetary warming (the so-called “RCP 2.6” IPCC scenario) we find that the frequency of QRA events remains roughly constant at current levels.
While we will presumably have to contend with many more summers like 2018 in the future, we could likely prevent any further increase in persistent summer weather extremes. In other words, the future is still very much in our hands when it comes to dangerous and damaging summer weather extremes. It’s simply a matter of our willpower to transition quickly from fossil fuels to renewable energy.
Do climate scientists ever read Popper? To test a theory we should look
not only at evidence supporting it but at evidence contradicting it. What is
the answer to the point that water vapor is a much more prevalent greenhouse
gas that carbon dioxide?
Query- genuine request for information, not an attempt to score debating points-
I believe there has been an increase in the number of days of daylight in the
Arctic and Antarctic, but I have not been able to find figures. This would
affect temperatures, but is obviously not related to CO2 and would indicate
one of the astronomical theories of climate change.
Re: MA Rodger 50: I guess we differ in our definition of “logic” which for me is about consistency of argument and ability to show that the observed results “make sense”.
In this case we have two arguments (i.e. two “logics”) attempting to explain why
atm vapour content does not keep up with temp (i.e. why the relative humidity drops). Graham: it is the lack of energy for evaporation; me: it is the lack of energy for evaporation
You haven’t proved the Grahma’s logic to be true – quite the opposite – your secondary argument invoking GISS moidel data seem to be “counter-logical” to his, not mine logic. You write:
“A closer look reveals that for a warming (in the GISS model at least) relative humidity increases slightly in the tropics, and decreases at mid latitudes..” The land at mid-latitudes is usually quite dry and of the deserty sort.”
To contradict my logic – the model would have somehow increase the availability of water for evaporation on dry land to see whether the relative humidity increases, thus proving my logic that it is lack of water for evaporation that is the holdup.
Oh, wait a minute – it did – the land in which increased availability of water for evaporation is there and is called … “ocean” (or “non-deserty type of land”): “humidity increases slightly in the tropics, and decreases at mid latitudes.. [these is more land in mid latitudes The land at mid-latitudes is usually quite dry and of the deserty sort.”
So the relative humidity is lower over dry land, where there is shortage “of water to evaporate”, than over ocean or wetlands where there is no such limitation. So those models are not so counter-logical after all … ;-)
Francis Knox – first of all, the role of water vapor is very well known, and a very, very simple search on this website could have answered your question.
Here’s one of the hits, an oldie (but goodie):
https://www.realclimate.org/index.php/archives/2005/04/water-vapour-feedback-or-forcing/
Then there’s your belief about the number of days of daylight on Antarctica and in the Arctic. Welcome to the Milankovitch cycles, with another relevant post on the Holocene here:
https://www.realclimate.org/index.php/archives/2013/09/paleoclimate-the-end-of-the-holocene/
#51, FK–
What Marco pointed to, but in short, the fact that it is not stable in the atmosphere, but condenses and precipitates out typically within days. Well, that and the fact that cold air doesn’t hold much moisture. The latter property would invoke a cooling/drying feedback cycle in the absence of other GHGs.
As a side note, it’s a bit amusing how some see Popper’s theories as entirely prescriptive for science. Given that he was only born in 1902, one might well wonder how science got on without him prior to, say, the publication of his first book in 1934.